Top 5 Wiki.js Alternatives
Looking for an alternative to WikiJS? You've come to the right place.
Wiki.js emerged as a powerful open-source wiki platform when it was first created by Nicolas Giard in 2016. Built on Node.js and written in JavaScript, WikiJS quickly gained popularity for its modern interface, multi-database support (PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, MS SQL Server, and SQLite), and powerful features like real-time collaboration, version control, and a visual WYSIWYG editor. Organizations worldwide adopted WikiJS for its blazing-fast performance, extensive authentication options, and ability to run on virtually any platform.
However, as WikiJS has evolved, many users have found themselves seeking alternatives. The platform's development trajectory and certain limitations have prompted teams to explore other options that better align with their evolving documentation needs.
Why Users Are Looking for Wiki JS Alternatives
Several significant issues have led users to search for Wiki.JS alternatives:
• Version 3.0 development limbo: WikiJS v3 has been in development since 2021, with a Developer Preview released in October 2022, but no beta has been released to date despite promises of it arriving "in the coming weeks/months." This extended development cycle has created uncertainty about the platform's future.
• Version 2.x in maintenance mode: The current stable version (2.x) is essentially in maintenance mode with no new features being added, as the development team focuses entirely on the elusive v3 release. This leaves users stuck with aging technology while waiting for promised improvements.
• UI bugs and user experience issues: Users consistently report UI bugs that "somewhat ruin the overall experience," making the platform less polished compared to alternatives.
• Limited collaborative features: Compared to competitors like Confluence and XWiki, WikiJS provides limited content collaboration and note-taking features.
Does that sound familiar? Then it might be time to switch. Fortunately, there are many great WikiJS alternatives to choose from.
Best 5 Wikijs Alternatives
To make your decision easier, we've put together a list of the best WikiJS alternatives and competitors, based on real reviews.
These open-source solutions offer various approaches to documentation and knowledge management, from simple file-based wikis to sophisticated collaborative platforms. Each brings unique strengths that address different pain points users experience with WikiJS.
Check out the list below and find the solution that best suits your needs.
Docmost
Docmost is an open-source wiki and documentation software designed for seamless real-time collaboration, allowing multiple users to work on the same page simultaneously without overwriting each other. Released under the AGPL-3.0 license, Docmost positions itself as a modern alternative to both Notion and Confluence, offering a fresh approach to knowledge base software that addresses many of WikiJS's limitations.
Unlike WikiJS's stalled development, Docmost maintains an active release cycle with regular updates and new features. The platform features a rich-text editor with real-time collaboration, built-in support for diagrams (Mermaid, Draw.io, and Excalidraw), and robust permissions management. This makes it ideal for teams that need powerful documentation tools with modern collaboration features that WikiJS v2 lacks.
Docmost's architecture includes Spaces for organizing content by teams, projects, or departments, each with its own permissions. The platform also supports importing and exporting pages in Markdown and HTML formats, and even includes importers for Confluence and Notion, ensuring no vendor lock-in. For organizations concerned about data sovereignty, Docmost can be self-hosted with support for both S3 and local storage drivers.
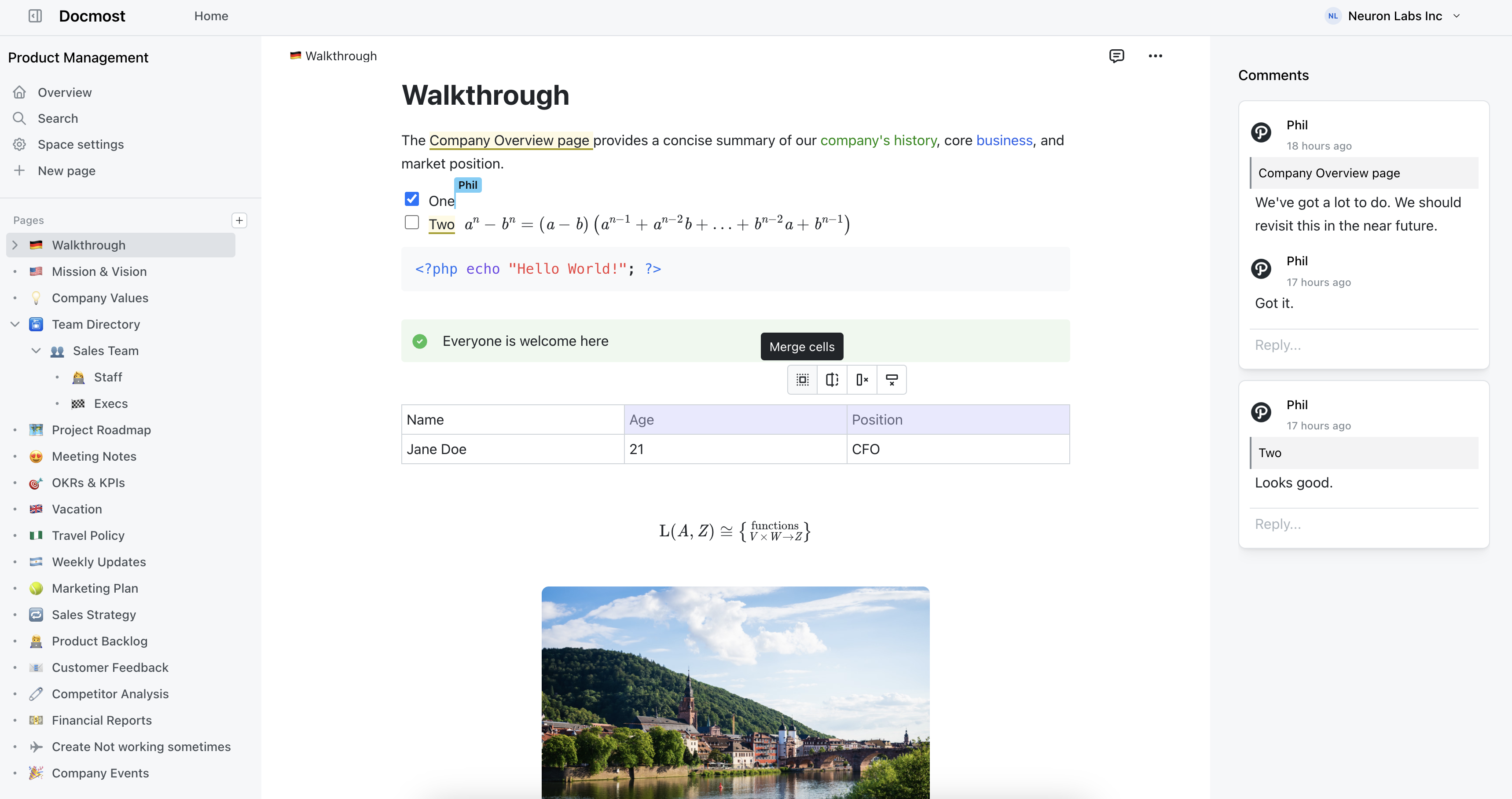
What sets Docmost apart is its focus on user experience and modern development practices. The platform features an integrated inline commenting system for meaningful discussions directly on pages, comprehensive page history with version tracking, and support for over 10 languages. Teams migrating from WikiJS will appreciate the seamless real-time collaboration that doesn't require page locking or manual conflict resolution.
Docmost features
- Collaborative Real-time Editor: Work together on pages in real time.
- Diagrams: Built-in support for Drawio, Excalidraw, and Mermaid diagramming tools.
- Spaces: Organize your pages by team, projects, or departments for better collaboration.
- Permissions Management: Easily control access to pages with easy-to-understand permissions.
- Groups: Easily grant unified permissions to users via groups.
- Comments: Add inline comments to pages for better communication and feedback.
- Page History: Track changes with a comprehensive version history.
- Nested Navigation: You can nest and reorder pages via the sidebar.
- Search: Quickly find the information you need with powerful search capabilities.
- File Attachment: Attach files to your pages for quick reference and sharing.
- Embeds: Embed content from Airtable, Loom, YouTube, and more.
- Authentication: Email and password + SSO login (SAML 2.0/OIDC) in the Enterprise edition.
AppFlowy
AppFlowy is an open-source collaborative workspace that brings a unique approach to the wiki landscape. Built with Flutter and Rust for cross-platform compatibility and performance, AppFlowy is released under the AGPL-3.0 license and positions itself as the leading open-source Notion alternative. For teams frustrated with WikiJS's limited innovation and slow development, AppFlowy represents a modern, actively developed alternative.
What distinguishes AppFlowy from traditional wikis like WikiJS is its focus on flexibility and local-first architecture. The platform works faster and more stable with support for offline mode, better device integration, and enables users to access features not available on the web. AppFlowy's commitment to user control means you can design and modify the platform your way, with 100% control of your data.
AppFlowy's feature set goes beyond traditional wiki functionality, offering LEGO-like building blocks for creating lists, tables, and formulas that define field behavior and relationships. The platform also supports self-hosting capabilities with comprehensive deployment options, giving organizations complete control over their infrastructure.
For organizations considering WikiJS alternatives, AppFlowy's modern architecture and active development community provide confidence in long-term viability. Unlike WikiJS's uncertain roadmap, AppFlowy maintains transparent development practices with regular releases and clear communication about upcoming features.
BookStack
BookStack is a simple, self-hosted platform written in PHP using the Laravel framework, released under the MIT License. Created by Dan Brown with its first commit published on July 12, 2015, BookStack has become the most popular wiki software written in PHP on GitHub with 16k stars as of July 2025. Its unique approach to organizing content using familiar concepts of books, chapters, and pages provides an intuitive structure that many find more approachable than traditional wiki hierarchies.
The platform features both a WYSIWYG editor and a Markdown editor with live preview, built-in Draw.io integration for diagramming, and the ability to link directly to any paragraph. This focus on user experience extends to features like configurable dark and light themes, multi-language support (over 30 languages), and various authentication options including social providers, SAML2, and LDAP.
BookStack excels in scenarios where teams need structured documentation management without complexity. The platform can run happily on a $5 Digital Ocean VPS, making it accessible for small teams and personal projects. Its REST API and visual theme system allow for customization without the need for extensive development.
For organizations evaluating WikiJS alternatives, BookStack's active development, clear documentation, and responsive community support stand in stark contrast to WikiJS's stalled progress. The developer Dan Brown has been outstanding in supporting his project across many platforms, contributing to BookStack's reputation as a reliable, well-maintained solution.
XWiki
XWiki is a mature, enterprise-grade wiki platform written in Java and released under the GNU Lesser General Public License. With development stretching back to 2007, XWiki has evolved into one of the most feature-rich open-source wiki platforms available. For organizations seeking a WikiJS alternative with proven enterprise capabilities and extensive customization options, XWiki presents a compelling choice.
What sets XWiki apart is its application wiki capabilities. As an application wiki, XWiki allows for storing structured data and executing server-side scripts within the wiki interface. Scripting languages including Velocity, Apache Groovy, Python, Ruby, and PHP can be written directly into wiki pages using wiki macros. This level of extensibility far exceeds what WikiJS offers, allowing teams to build custom applications and workflows directly within their documentation platform.
XWiki includes enterprise features like advanced authentication mechanisms (Form, Basic, LDAP, Custom), powerful rights management at the wiki/space/page level, and support for importing various formats including Office documents. The platform's rendering engine can parse multiple wiki syntaxes including Confluence, MediaWiki, and TWiki, making migration from other platforms straightforward. For large organizations, XWiki's proven scalability and extensive API make it suitable for enterprise knowledge management at scale.
XWiki's active development and clear roadmap provide the stability and predictability that WikiJS currently lacks.
DokuWiki
DokuWiki is a mature, lightweight wiki software created by Andreas Gohr in June 2004. Written in PHP and licensed under GPLv2, it takes a fundamentally different approach from WikiJS by storing all content in plain text files rather than requiring a database. This design choice makes DokuWiki extremely portable and easy to maintain, addressing one of the common pain points with database-dependent wikis like WikiJS.
For teams frustrated with WikiJS's complexity and database requirements, DokuWiki offers refreshing simplicity. The platform can be installed on local PCs, flash drives, and folders synced with file hosting services like Dropbox or Syncthing. This flexibility makes it ideal for personal wikis and scenarios where you need offline access.
DokuWiki includes powerful features like detailed access control lists (ACLs) for fine-grained permissions, full version history with diff viewing, and support for over 70 languages. The platform's extensive plugin ecosystem (over 1,000 plugins available) allows teams to extend functionality without waiting for core updates—a stark contrast to WikiJS v2's feature freeze. Built-in features include indexed search, two-level caching for performance, and support for multiple authentication backends including LDAP and Active Directory.
What makes DokuWiki particularly attractive for enterprise environments is its proven stability and lightweight footprint. The platform can run on minimal resources, and its text-file storage means backups are as simple as copying files.
We hope this list helps you narrow down your options and find the perfect WikiJS replacement for you and your team.